History
article | Reading time5 min
History
article | Reading time5 min
Follow the story of the creation of the Avenue des Champs-Élysées, and the origins of the Arc de Triomphe.
The first major works on what was to become the Avenue des Champs-Élysées and the Place de l'Étoile date back to 1667.
It was gardener André Le Nôtre who commissioned King Louis XIV to create a perspective from the Palais des Tuileries to the hill of Chaillot (now Place de l'Étoile).
The main axis of this new perspective garden was the route to the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye.
Known as the " Grand Cour ", these perspective gardens were laid out on marshy land and extended as far as the Chaillot hill.
In 1709, the lower part of the Grand Cour was renamed Champs-Élysées, in reference to one of the divisions of the Underworld in Greco-Roman mythology.
Bibliothèque nationale de France, Prints and Photography Department
In 1758, engineer Jean-Etienne Ribart de Chamoust proposed to complete the Champs-Élysées perspective with a monumental sculpture. He sent the king a proposal for a sixty-meter elephant-watercourse.
Fed by the basins of La Villette, a fountain was to spring from the animal's trunk. Inside, there would be concert halls, dance halls and apartments dedicated to the Kingdom's official visitors.
A statue of the king was to rise to the top, surrounded by flags and lions, but Louis XV refused the project, arguing that the statue celebrated Hannibal's glory far more than his own victories.
Reproduction Philippe Berthé / Centre des monuments nationaux
A few years later, engineer Jean-Rodolphe Perronet began levelling the hill. This lowered the level by 16 feet (4 to 5 meters). The Colline de Chaillot, at the end of the Champs-Élysées, was renamed the Promenoir, but no construction was planned.
Under Louis XVI, a tax was introduced at the entrance to the city of Paris. In 1785, octroi gates were erected all around the capital, including on the Promenoir de Chaillot. Designed by Ledoux, this section of the fermiers généraux' wall stood at the western end of the Champs-Élysées.
In 1798, the Directoire Minister of the Interior, François de Neufchâteau, organized a major architectural competition. His ambition was to complete the Champs-Élysées perspective with an emblematic building. Thirteen projects were submitted, but no further action was taken.
Reproduction Patrick Cadet / Centre des monuments nationaux
Consecrated in 1804, Napoleon I led major military campaigns with his Grande Armée. The day after the Battle of Austerlitz, in December 1805, he instructed his Minister of the Interior, Jean-Baptiste Nompère de Champagny, to begin urgent work on a triumphal arch to the glory of his soldiers.
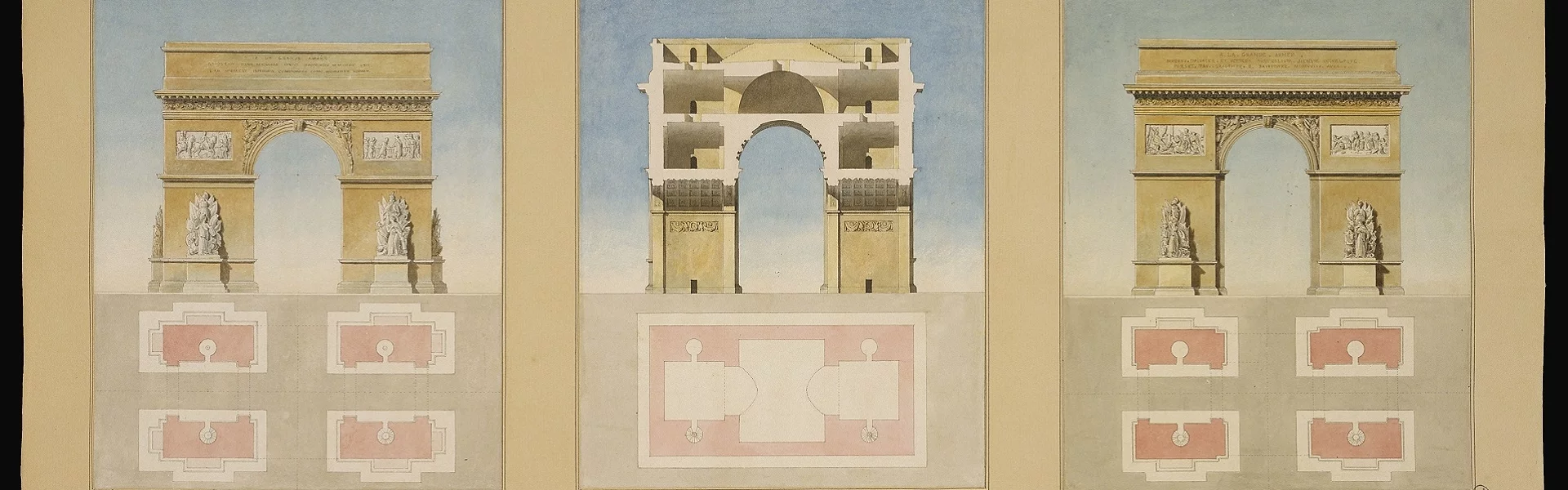
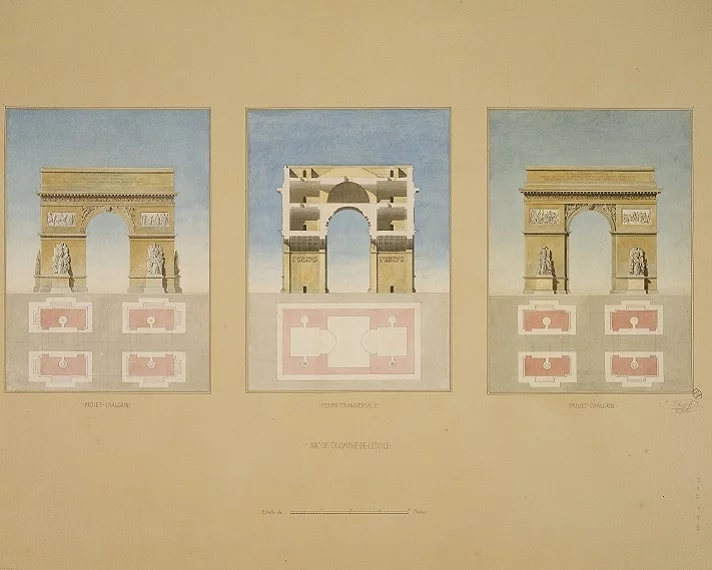
On February 18, 1806, Napoleon signed an imperial decree ordering the erection of an arch in honor of the Grande Armée. Architect Jean-François Thérèse Chalgrin, assisted by Jean-Arnaud Raymond, drew up the initial plans.
The question of where to place the arch was still unresolved. The Place de la Bastille came to mind, but the roads did not intersect geometrically. Three months later, Napoleon accepted the architects' proposal and decided to build the Arc de Triomphe to the west of the Champs-Élysées, so that it could be seen from the Palais des Tuileries (the imperial residence).
Bibliothèque nationale de France, Prints and Photography Department.
Reproduction Philippe Berthé / Centre des monuments nationaux
Reproduction Philippe Berthé / Centre des monuments nationaux
On August 15, 1806, Emperor Napoleon I's birthday, the foundation stone of the building was laid at a depth of eight meters, between the two southern pillars. On the lead sheet covering the stone, the inscription reads:
M. de Champagny
Reproduction Philippe Berthé / Centre des monuments nationaux